🤔 From Manual Work to Machine Intelligence
Why Supply Chain Leaders Must Rebuild Trust in Technology Before It's Too Late
Manual work has become the quiet bottleneck of the global supply chain, especially across Europe. While AI is rewriting the rules of planning, forecasting, procurement, and logistics, many Supply Chain Managers, Planners, and Directors continue to operate as if we’re still in 2005: stuck in spreadsheets, reliant on tribal knowledge, and disconnected from real-time systems.
And it's not for lack of tools.
It's because of something deeper: a breakdown in trust.
🔍 The Trust Collapse in Supply Chain Technology
Despite an explosion in AI and cloud innovation, many supply chain professionals remain skeptical. Why?
Because they've been promised "transformation" for years - and nothing changed. ERP upgrades failed. Visibility platforms underdelivered. Dashboards cluttered instead of clarified.
So they defaulted to what they know: Excel. Emails. Manual firefighting.
But now the stakes are different.
AI is no longer a buzzword. It's a fully deployable layer of intelligence. And supply chains that delay adoption aren't just inefficient - they're becoming structurally uncompetitive.
The Silent Struggle: How Supply Chain Leaders Can Rebuild Trust in Technology Before It’s Too Late
📊 From Overwhelm to Ownership: Rethinking the AI Journey
One reader recently shared:
“It’s easy to feel overwhelmed by all the AI opportunities. A good tip is to enjoy learning about it, not just treat it as something you have to learn.”
That mindset shift - from resistance to curiosity - is the real unlock. And it’s essential for modern supply chain leaders.
To guide this transformation, I’ve written extensively about how to embrace AI without losing control:
Are Supply Chain Managers & Planners Ready for the AI Shift?
Are Supply Chain Managers Ready to Ditch Manual Work for AI?
The Future of Supply Chain: From Manual Chaos to AI-Driven Excellence
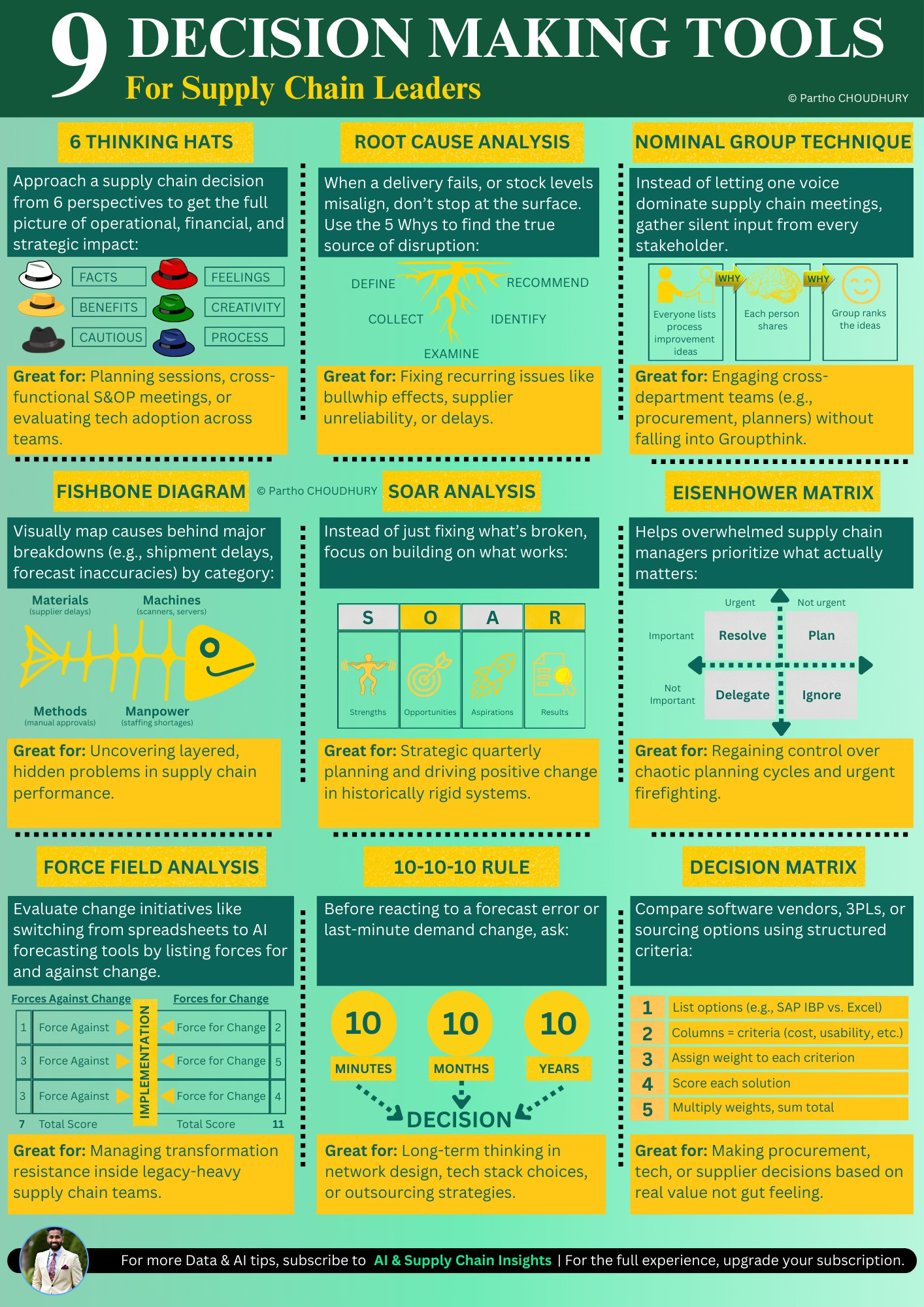
⚖️ 9 Decision-Making Tools Every Supply Chain Leader Should Be Using
Why frameworks - not just instinct - are the competitive edge in a complex, AI-powered era
Operating a supply chain in 2025 means navigating uncertainty: volatile demand, geopolitical risk, tech overload, and organizational inertia. The difference between leaders who thrive and those who stall?
They don’t rely solely on experience. They use structured thinking tools - mental models that bring clarity to chaos.
Here are 9 of the most effective tools, with insights from their original creators and how they translate to the supply chain world:
1. 🎩 Six Thinking Hats (Edward de Bono)
Purpose: To explore decisions from six distinct mindsets, promoting balanced and creative thinking.
Application in Supply Chain:
Use this in S&OP meetings or cross-functional reviews when evaluating tech adoption, new distribution models, or major procurement shifts.
White Hat (Facts & data): What does the current demand data say?
Red Hat (Emotions): How do stakeholders feel about the AI rollout?
Black Hat (Caution): What could go wrong with the implementation?
Yellow Hat (Optimism): What benefits might we unlock?
Green Hat (Creativity): Is there an unconventional supplier or model to consider?
Blue Hat (Process): How will we structure the decision-making process?
✅ Great for: Avoiding blind spots, getting full team buy-in, and managing risk in collaborative decisions.
2. 🪜 Root Cause Analysis / 5 Why’s (Toyota Production System, Taiichi Ohno)
Purpose: To dig beneath surface-level symptoms and find the true cause of recurring problems.
Supply Chain Use Case:
If forecast accuracy keeps falling short, don’t just blame the data. Ask why - 5 times. For example:
Why were shipments late? → Because forecasts were inaccurate.
Why were forecasts inaccurate? → Because planners didn’t trust the AI model.
Why not? → Because past models failed to deliver.
Why did they fail? → They weren’t trained on current demand patterns.
Why weren’t they retrained? → There was no ownership process for model updates.
✅ Great for: Continuous improvement and diagnosing persistent issues like stockouts, supplier failures, or planning breakdowns.
3. ✍️ Nominal Group Technique (Andre Delbecq & Andrew Van de Ven)
Purpose: Structured idea generation that promotes equal participation and avoids dominant voices.
How to use in Supply Chain:
During transformation planning or vendor evaluation workshops, let team members submit ideas anonymously, then share and rank together.
✅ Great for: Multi-location teams, cross-functional planning, and inclusive decision-making.
4. 🐟 Fishbone Diagram / Ishikawa Diagram (Kaoru Ishikawa)
Purpose: To visually map the potential causes of a problem in categorized “bones.”
Supply Chain Application:
Use this tool to dissect a quality issue, late delivery trend, or operational bottleneck. Structure causes under:
People (Training, resistance)
Process (Manual inputs, outdated SOPs)
Technology (Legacy tools, poor integrations)
Materials (Vendor issues, supply shortages)
✅ Great for: Diagnosing process failures and preparing cross-functional workshops.
5. 🌱 SOAR Analysis (Stavros & Hinrichs)
Purpose: A forward-looking alternative to SWOT - focusing on building from what’s strong, not just fixing what’s broken.
Supply Chain Relevance:
Frame your digital roadmap around what’s working well:
Strengths: Agile local teams, reliable partners
Opportunities: New AI forecasting tools, regional trade incentives
Aspirations: Faster replenishment, smarter fulfillment
Results: KPI alignment (e.g., OTIF, service levels, CO2 reduction)
✅ Great for: Vision-setting sessions, tech rollouts, or transformation playbooks.
6. 🧭 Eisenhower Matrix (Dwight D. Eisenhower)
Purpose: Time management and priority alignment: Urgent vs. Important
Supply Chain Use:
In a world of constant emails, alerts, and meetings, this helps planners and leaders focus on high-impact tasks.
Urgent & Important: Fix today’s disruption
Important, Not Urgent: Redesign the replenishment model
Urgent, Not Important: Vendor update request → delegate
Neither: Ignore low-value reporting tasks
✅ Great for: Time-blocking, managing chaos, and avoiding firefighting culture.
7. ⚖️ Force Field Analysis (Kurt Lewin)
Purpose: Assess forces pushing for or against a proposed change.
Use in Supply Chain:
Planning an AI implementation? Map the driving and resisting forces:
Forces For: Leadership support, vendor experience, potential ROI
Forces Against: Team resistance, budget risk, lack of training
Balance the list, then decide how to amplify positives and neutralize negatives.
✅ Great for: Change management and tech adoption strategies.
8. ⏳ 10-10-10 Rule (Suzy Welch)
Purpose: Gain perspective by evaluating consequences at three time scales: 10 minutes, 10 months, and 10 years.
Supply Chain Example:
Thinking of outsourcing planning to a BPO?
In 10 minutes: It relieves the team
In 10 months: We risk losing internal capability
In 10 years: We might lose strategic agility
✅ Great for: Long-term supply chain design decisions.
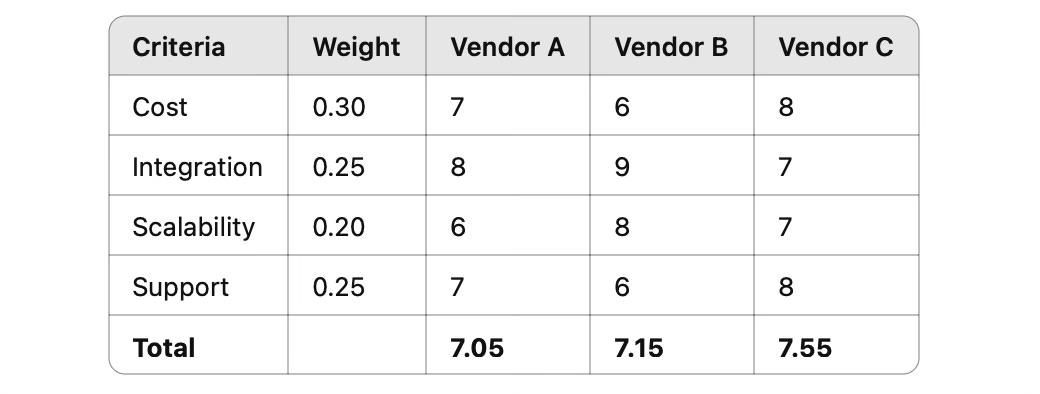
9. 📊 Decision Matrix / Weighted Scoring Model
Purpose: Objectively compare multiple options using criteria and weights.
How to Use:
Compare AI tools, 3PL partners, or demand planning solutions. Assign:
Rows: Options (Vendor A, B, C)
Columns: Criteria (Cost, Integration, Scalability, Support)
Weights: Importance of each
Scores: Rate each, multiply by weights, total them
📊 Decision Matrix Formula
Use this method to compare multiple supply chain options - like AI tools, 3PL partners, or planning systems - based on weighted criteria.
Step-by-Step Formula
1. List Options: Define each row as a decision option:
→ Vendor A, Vendor B, Vendor C
2. Define Criteria: Create columns for key decision factors:
→ Cost, Integration, Scalability, Support
3. Assign Weights: Allocate importance to each criterion (total = 1):
Cost = 0.30
Integration = 0.25
Scalability = 0.20
Support = 0.25
4. Score Each Option: Rate each vendor on a consistent scale (e.g., 1–10).
5. Apply the Formula
✅ Example
🧠 Use this formula to remove bias, bring transparency, and align your team around smart, data-driven decisions.
✅ Great for: Tech vendor selection, procurement strategy, or warehouse automation planning.
🎯 Why These Tools Matter
In fast-moving supply chains, the illusion of control is tempting. But true leadership is built on structured thinking in ambiguous conditions.
These tools help supply chain professionals move from:
Reaction → Reflection
Gut feeling → Collective clarity
Manual bias → Data-led trust
They’re not magic. But they’re proven, repeatable, and incredibly relevant - especially for leaders trying to rebuild trust in technology while navigating change.
🎓 12 Real-World Case Studies for Supply Chain Leaders
Here are 12 handpicked case studies showing how organizations moved from manual to intelligent systems:
📊 Final Thought
The manual default is no longer safe.
Europe’s supply chains don’t just need technology - they need trust, strategy, and tools for real adoption.
If you’re leading a supply chain team, ask yourself:
Are we operating like it's 2025, or still stuck in 2012?
The shift won’t come from tools alone. It starts with mindset, method, and trust rebuilt.
Quote/Unquote
“We didn’t resist technology because we were afraid of it. We resisted because nothing ever changed. But now - AI is showing us results we can’t ignore.”
—European Supply Chain Director, on rebuilding trust in technology after a decade of digital fatigue.
Get Ready for Game-Changing Innovations in 2025! 🌟
Stay ahead of the curve with these groundbreaking updates and reports from Supplia:
🔹 Q3 2025:
• AI-Powered Supply Chain Transformation: Watch as Supplia takes supply chain management to the next level with advanced AI and automation tools.
• Insightful Research: Exclusive industry research on AI and cloud integration to optimize supply chain performance.
🔹 Q4 2025:
• Revolutionary AI & Automation Features: Unveiling Supplia’s next-generation AI-powered solutions that will change the way you manage Planning & Distribution.
• Supply Chain Optimization Report: A deep dive into cutting-edge strategies for streamlining your supply chain.
🔹 Q1 2026:
• Sustainability in Supply Chains: Get the latest data and trends on sustainable practices, focusing on how AI can reduce emissions and improve efficiency.
• Major Platform Update: A monumental update to Supplia’s platform, enhancing capabilities and ensuring a future-ready supply chain.
🔹 Q2 2026:
• AI-Driven Supply Chain Evolution: The next chapter of Supplia’s AI evolution, enabling predictive insights and smarter decision-making.
• Annual Industry Snapshot: A comprehensive look at the state of supply chain technology and its future.
Stay tuned and be part of the revolution! 🚀
🚀 Be First to Know
We’re preparing to launch the product designed to help supply chain leaders embrace AI with confidence - built on everything you’ve been reading here.
🔔 Want to be notified the moment it goes live?
Click here to get notified on Product Hunt.
Let’s shape the future of supply chain - together.